Image segmentation with UNETR model#
This tutorial demonstrates how to implement and train a model on image segmentation task. Below, we will be using the Oxford Pets dataset containing images and masks of cats and dogs. We will implement from scratch the UNETR model using Flax NNX. We will train the model on a training set and compute image segmentation metrics on the training and validation sets. We will use Orbax checkpoint manager to store best models during the training.
Prepare image segmentation dataset and dataloaders#
In this section we use the Oxford Pets dataset. We download images and masks and provide a code to work with the dataset. This approach can be easily extended to any image segmentation datasets and users can reuse this code for their own datasets.
In the code below we make a choice of using OpenCV and Pillow to read images and masks as NumPy arrays, Albumentations for data augmentations and
grain for batched data loading. Alternatively, one can use tensorflow_dataset or torchvision for the same task.
Requirements installation#
We will need to install the following Python packages:
!pip install -U opencv-python-headless grain albumentations Pillow
!pip install -U flax optax orbax-checkpoint
import jax
import flax
import optax
import orbax.checkpoint as ocp
print("Jax version:", jax.__version__)
print("Flax version:", flax.__version__)
print("Optax version:", optax.__version__)
print("Orbax version:", ocp.__version__)
Jax version: 0.4.34
Flax version: 0.10.1
Optax version: 0.2.4
Orbax version: 0.9.1
Data download#
Let’s download the data and extract images and masks.
!rm -rf /tmp/data/oxford_pets
!mkdir -p /tmp/data/oxford_pets
!wget https://thor.robots.ox.ac.uk/datasets/pets/images.tar.gz -O /tmp/data/oxford_pets/images.tar.gz
!wget https://thor.robots.ox.ac.uk/datasets/pets/annotations.tar.gz -O /tmp/data/oxford_pets/annotations.tar.gz
!cd /tmp/data/oxford_pets && tar -xf images.tar.gz
!cd /tmp/data/oxford_pets && tar -xf annotations.tar.gz
!ls /tmp/data/oxford_pets
We can also inspect the downloaded images folder, listing a subset of these files:
!ls /tmp/data/oxford_pets/images | wc -l
!ls /tmp/data/oxford_pets/images | head
!ls /tmp/data/oxford_pets/annotations/trimaps | wc -l
!ls /tmp/data/oxford_pets/annotations/trimaps | head
7393
Abyssinian_1.jpg
Abyssinian_10.jpg
Abyssinian_100.jpg
Abyssinian_100.mat
Abyssinian_101.jpg
Abyssinian_101.mat
Abyssinian_102.jpg
Abyssinian_102.mat
Abyssinian_103.jpg
Abyssinian_104.jpg
ls: write error: Broken pipe
7390
Abyssinian_1.png
Abyssinian_10.png
Abyssinian_100.png
Abyssinian_101.png
Abyssinian_102.png
Abyssinian_103.png
Abyssinian_104.png
Abyssinian_105.png
Abyssinian_106.png
Abyssinian_107.png
ls: write error: Broken pipe
Train/Eval datasets#
Let’s implement the dataset class providing the access to the images and masks. The class implements __len__ and __getitem__ methods.
In this example, we do not have a hard training and validation data split, so we will use the total dataset and make a random training/validation split by indices.
For this purpose we provide a helper class to map indices into training and validation parts.
from typing import Any
from pathlib import Path
import cv2
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image # we'll read images with opencv and use Pillow as a fallback
class OxfordPetsDataset:
def __init__(self, path: Path):
assert path.exists(), path
self.path: Path = path
self.images = sorted((self.path / "images").glob("*.jpg"))
self.masks = [
self.path / "annotations" / "trimaps" / path.with_suffix(".png").name
for path in self.images
]
assert len(self.images) == len(self.masks), (len(self.images), len(self.masks))
def __len__(self) -> int:
return len(self.images)
def read_image_opencv(self, path: Path):
img = cv2.imread(str(path))
if img is not None:
return cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
else:
None
def read_image_pillow(self, path: Path):
img = Image.open(str(path))
img = img.convert("RGB")
return np.asarray(img)
def read_mask(self, path: Path):
mask = cv2.imread(str(path), cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
# mask has values: 1, 2, 3
# 1 - object mask
# 2 - background
# 3 - boundary
# Define mask as 0-based int values
mask = mask - 1
return mask.astype("uint8")
def __getitem__(self, index: int) -> dict[str, np.ndarray]:
img_path, mask_path = self.images[index], self.masks[index]
img = self.read_image_opencv(img_path)
if img is None:
# Fallback to Pillow if OpenCV fails to read an image
img = self.read_image_pillow(img_path)
mask = self.read_mask(mask_path)
return {
"image": img,
"mask": mask,
}
class SubsetDataset:
def __init__(self, dataset, indices: list[int]):
# Check input indices values:
for i in indices:
assert 0 <= i < len(dataset)
self.dataset = dataset
self.indices = indices
def __len__(self) -> int:
return len(self.indices)
def __getitem__(self, index: int) -> Any:
i = self.indices[index]
return self.dataset[i]
Now, let’s define the total dataset and compute data indices for training and validation splits:
seed = 12
train_split = 0.7
dataset_path = Path("/tmp/data/oxford_pets")
dataset = OxfordPetsDataset(dataset_path)
rng = np.random.default_rng(seed=seed)
le = len(dataset)
data_indices = list(range(le))
# Let's remove few indices corresponding to corrupted images
# to avoid libjpeg warnings during the data loading
corrupted_data_indices = [3017, 3425]
for index in corrupted_data_indices:
data_indices.remove(index)
random_indices = rng.permutation(data_indices)
train_val_split_index = int(train_split * le)
train_indices = random_indices[:train_val_split_index]
val_indices = random_indices[train_val_split_index:]
# Ensure there is no overlapping
assert len(set(train_indices) & set(val_indices)) == 0
train_dataset = SubsetDataset(dataset, indices=train_indices)
val_dataset = SubsetDataset(dataset, indices=val_indices)
print("Training dataset size:", len(train_dataset))
print("Validation dataset size:", len(val_dataset))
Training dataset size: 5173
Validation dataset size: 2215
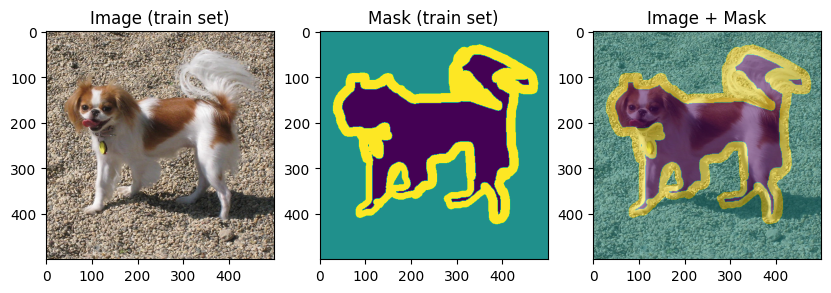
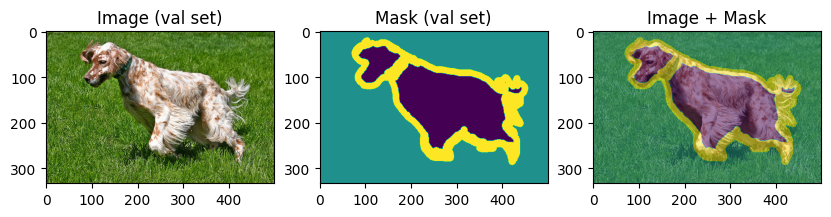
To verify our work so far, let’s display few training and validation images and masks:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def display_datapoint(datapoint, label=""):
img, mask = datapoint["image"], datapoint["mask"]
if img.dtype in (np.float32, ):
img = ((img - img.min()) / (img.max() - img.min()) * 255.0).astype(np.uint8)
fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=(10, 10))
axs[0].set_title(f"Image{label}")
axs[0].imshow(img)
axs[1].set_title(f"Mask{label}")
axs[1].imshow(mask)
axs[2].set_title("Image + Mask")
axs[2].imshow(img)
axs[2].imshow(mask, alpha=0.5)
display_datapoint(train_dataset[0], label=" (train set)")
display_datapoint(val_dataset[0], label=" (val set)")
Data augmentations#
Next, let’s define a simple data augmentation pipeline of joined image and mask transformations using Albumentations. We apply geometric and color transformations to increase the diversity of the training data. For more details on the Albumentations transformations, we can check Albumentations reference API.
import albumentations as A
img_size = 256
train_transforms = A.Compose([
A.Affine(rotate=(-35, 35), cval_mask=1, p=0.3), # Random rotations -35 to 35 degrees
A.RandomResizedCrop(width=img_size, height=img_size, scale=(0.7, 1.0)), # Crop a random part of the input and rescale it to a specified size
A.HorizontalFlip(p=0.5), # Horizontal random flip
A.RandomBrightnessContrast(p=0.4), # Randomly changes the brightness and contrast
A.Normalize(), # Normalize the image and cast to float
])
val_transforms = A.Compose([
A.Resize(width=img_size, height=img_size),
A.Normalize(), # Normalize the image and cast to float
])
output = train_transforms(**train_dataset[0])
img, mask = output["image"], output["mask"]
print("Image array info:", img.dtype, img.shape, img.min(), img.mean(), img.max())
print("Mask array info:", mask.dtype, mask.shape, mask.min(), mask.max())
Image array info: float32 (256, 256, 3) -1.5356623 0.5732621 2.6399999
Mask array info: uint8 (256, 256) 0 2
output = val_transforms(**val_dataset[0])
img, mask = output["image"], output["mask"]
print("Image array info:", img.dtype, img.shape, img.min(), img.mean(), img.max())
print("Mask array info:", mask.dtype, mask.shape, mask.min(), mask.max())
Image array info: float32 (256, 256, 3) -2.117904 -0.30076745 2.6399999
Mask array info: uint8 (256, 256) 0 2
Data loaders#
Let’s now use grain to perform data loading, augmentations and batching on a single device using multiple workers. We will create a random index sampler for training and an unshuffled sampler for validation.
from typing import Any, Callable
import grain.python as grain
class DataAugs(grain.MapTransform):
def __init__(self, transforms: Callable):
self.albu_transforms = transforms
def map(self, data):
output = self.albu_transforms(**data)
return output
train_batch_size = 72
val_batch_size = 2 * train_batch_size
# Create an IndexSampler with no sharding for single-device computations
train_sampler = grain.IndexSampler(
len(train_dataset), # The total number of samples in the data source
shuffle=True, # Shuffle the data to randomize the order of samples
seed=seed, # Set a seed for reproducibility
shard_options=grain.NoSharding(), # No sharding since this is a single-device setup
num_epochs=1, # Iterate over the dataset for one epoch
)
val_sampler = grain.IndexSampler(
len(val_dataset), # The total number of samples in the data source
shuffle=False, # Do not shuffle the data
seed=seed, # Set a seed for reproducibility
shard_options=grain.NoSharding(), # No sharding since this is a single-device setup
num_epochs=1, # Iterate over the dataset for one epoch
)
train_loader = grain.DataLoader(
data_source=train_dataset,
sampler=train_sampler, # Sampler to determine how to access the data
worker_count=4, # Number of child processes launched to parallelize the transformations among
worker_buffer_size=2, # Count of output batches to produce in advance per worker
operations=[
DataAugs(train_transforms),
grain.Batch(train_batch_size, drop_remainder=True),
]
)
# Validation dataset loader
val_loader = grain.DataLoader(
data_source=val_dataset,
sampler=val_sampler, # Sampler to determine how to access the data
worker_count=4, # Number of child processes launched to parallelize the transformations among
worker_buffer_size=2,
operations=[
DataAugs(val_transforms),
grain.Batch(val_batch_size),
]
)
# Training dataset loader for evaluation (without dataaugs)
train_eval_loader = grain.DataLoader(
data_source=train_dataset,
sampler=train_sampler, # Sampler to determine how to access the data
worker_count=4, # Number of child processes launched to parallelize the transformations among
worker_buffer_size=2, # Count of output batches to produce in advance per worker
operations=[
DataAugs(val_transforms),
grain.Batch(val_batch_size),
]
)
train_batch = next(iter(train_loader))
val_batch = next(iter(val_loader))
print("Train images batch info:", type(train_batch["image"]), train_batch["image"].shape, train_batch["image"].dtype)
print("Train masks batch info:", type(train_batch["mask"]), train_batch["mask"].shape, train_batch["mask"].dtype)
Train images batch info: <class 'grain._src.python.shared_memory_array.SharedMemoryArray'> (72, 256, 256, 3) float32
Train masks batch info: <class 'grain._src.python.shared_memory_array.SharedMemoryArray'> (72, 256, 256) uint8
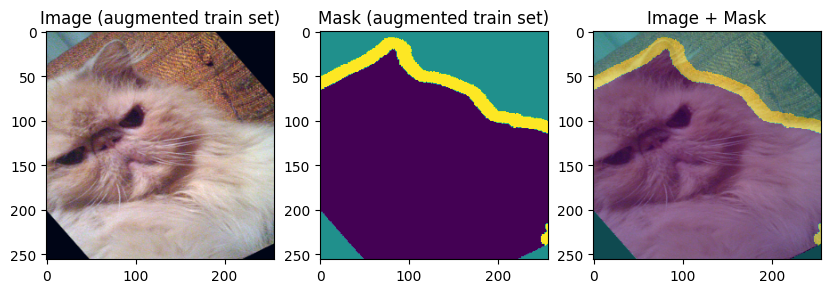
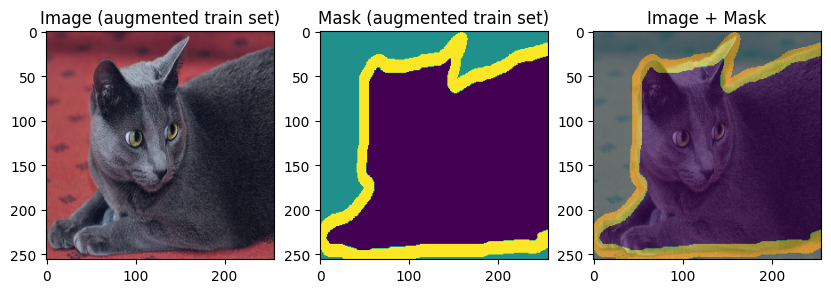
Finally, let’s display the training and validation data:
images, masks = train_batch["image"], train_batch["mask"]
for img, mask in zip(images[:3], masks[:3]):
display_datapoint({"image": img, "mask": mask}, label=" (augmented train set)")
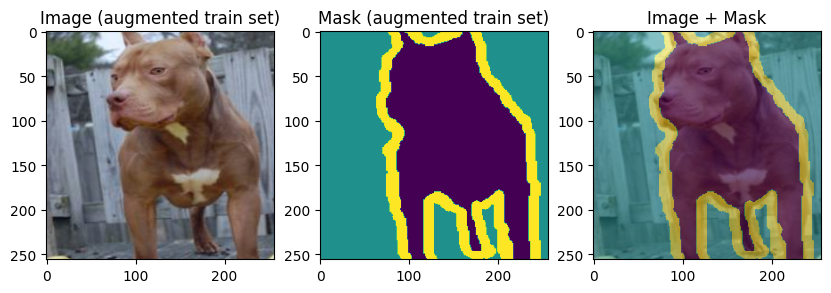
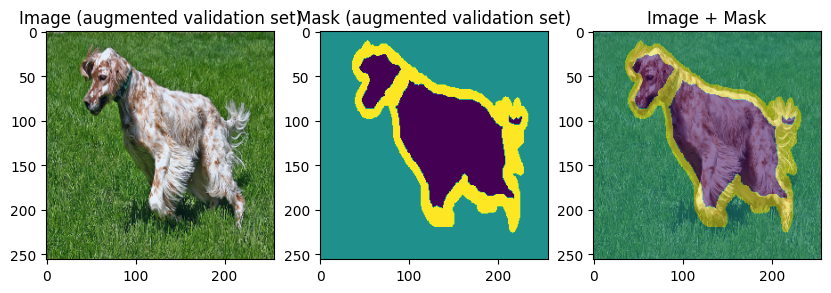
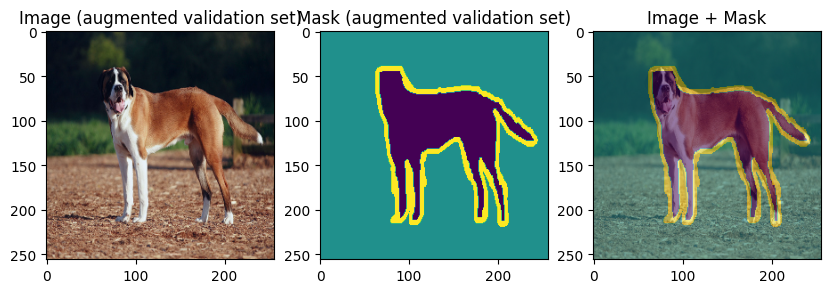
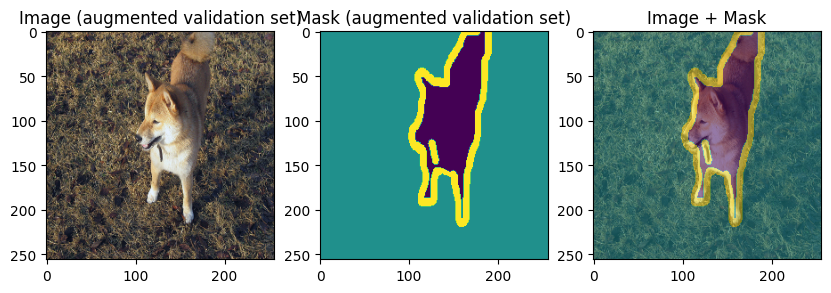
images, masks = val_batch["image"], val_batch["mask"]
for img, mask in zip(images[:3], masks[:3]):
display_datapoint({"image": img, "mask": mask}, label=" (augmented validation set)")
Model for Image Segmentation#
In this section we will implement the UNETR model from scratch using Flax NNX. The reference PyTorch implementation of this model can be found on the MONAI Library GitHub repository.
The UNETR model utilizes a transformer as the encoder to learn sequence representations of the input and to capture the global multi-scale information, while also following the “U-shaped” network design like UNet model:
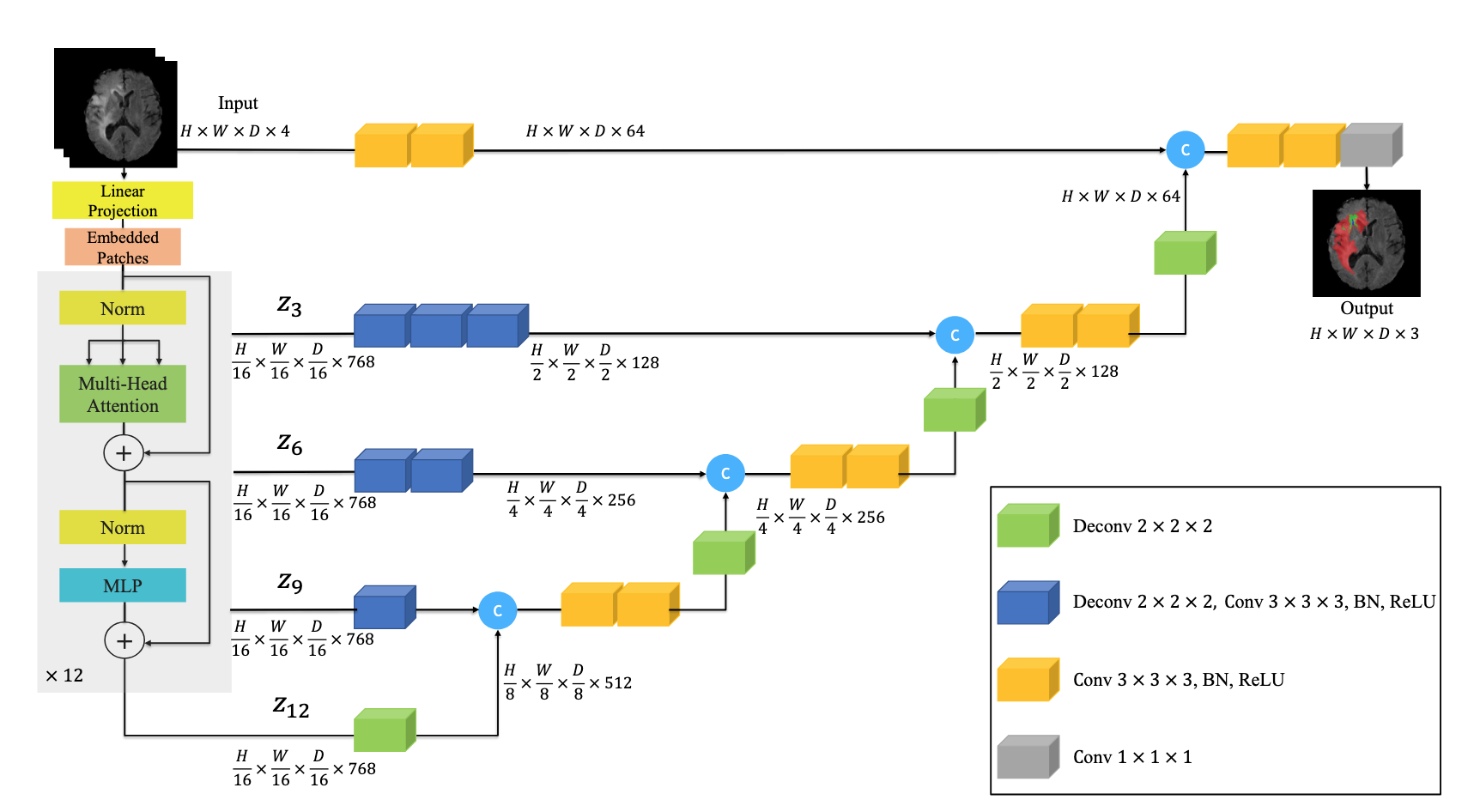
The UNETR architecture on the image above is processing 3D inputs, but it can be easily adapted to 2D input.
The transformer encoder of UNETR is Vision Transformer (ViT). The feature maps returned by ViT have all the same spatial size: (H / 16, W / 16) and deconvolutions are used to upsample the feature maps. Finally, the feature maps are upsampled and concatenated up to the original image size.
from flax import nnx
import jax.numpy as jnp
Vision Transformer encoder implementation#
Below, we will implement the following modules:
Vision Transformer,
ViTPatchEmbeddingBlock: patch embedding block, which maps patches of pixels to a sequence of vectorsViTEncoderBlock: vision transformer encoder blockMLPBlock: multilayer perceptron block
class PatchEmbeddingBlock(nnx.Module):
"""
A patch embedding block, based on: "Dosovitskiy et al.,
An Image is Worth 16x16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale <https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11929>"
"""
def __init__(
self,
in_channels: int, # dimension of input channels.
img_size: int, # dimension of input image.
patch_size: int, # dimension of patch size.
hidden_size: int, # dimension of hidden layer.
dropout_rate: float = 0.0,
*,
rngs: nnx.Rngs = nnx.Rngs(0),
):
n_patches = (img_size // patch_size) ** 2
self.patch_embeddings = nnx.Conv(
in_channels,
hidden_size,
kernel_size=(patch_size, patch_size),
strides=(patch_size, patch_size),
padding="VALID",
use_bias=True,
rngs=rngs,
)
initializer = jax.nn.initializers.truncated_normal(stddev=0.02)
self.position_embeddings = nnx.Param(
initializer(rngs.params(), (1, n_patches, hidden_size), jnp.float32)
)
self.dropout = nnx.Dropout(dropout_rate, rngs=rngs)
def __call__(self, x: jax.Array) -> jax.Array:
x = self.patch_embeddings(x)
x = x.reshape(x.shape[0], -1, x.shape[-1])
embeddings = x + self.position_embeddings
embeddings = self.dropout(embeddings)
return embeddings
mod = PatchEmbeddingBlock(3, 256, 16, 768, 0.5)
x = jnp.ones((4, 256, 256, 3))
y = mod(x)
print(y.shape)
(4, 256, 768)
from typing import Callable
class MLPBlock(nnx.Sequential):
"""
A multi-layer perceptron block, based on: "Dosovitskiy et al.,
An Image is Worth 16x16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale <https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11929>"
"""
def __init__(
self,
hidden_size: int, # dimension of hidden layer.
mlp_dim: int, # dimension of feedforward layer
dropout_rate: float = 0.0,
activation_layer: Callable = nnx.gelu,
*,
rngs: nnx.Rngs = nnx.Rngs(0),
):
layers = [
nnx.Linear(hidden_size, mlp_dim, rngs=rngs),
activation_layer,
nnx.Dropout(dropout_rate, rngs=rngs),
nnx.Linear(mlp_dim, hidden_size, rngs=rngs),
nnx.Dropout(dropout_rate, rngs=rngs),
]
super().__init__(*layers)
mod = MLPBlock(768, 3072, 0.5)
x = jnp.ones((4, 256, 768))
y = mod(x)
print(y.shape)
(4, 256, 768)
class ViTEncoderBlock(nnx.Module):
"""
A transformer encoder block, based on: "Dosovitskiy et al.,
An Image is Worth 16x16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale <https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11929>"
"""
def __init__(
self,
hidden_size: int, # dimension of hidden layer.
mlp_dim: int, # dimension of feedforward layer.
num_heads: int, # number of attention heads
dropout_rate: float = 0.0,
*,
rngs: nnx.Rngs = nnx.Rngs(0),
) -> None:
self.mlp = MLPBlock(hidden_size, mlp_dim, dropout_rate, rngs=rngs)
self.norm1 = nnx.LayerNorm(hidden_size, rngs=rngs)
self.attn = nnx.MultiHeadAttention(
num_heads=num_heads,
in_features=hidden_size,
dropout_rate=dropout_rate,
broadcast_dropout=False,
decode=False,
rngs=rngs,
)
self.norm2 = nnx.LayerNorm(hidden_size, rngs=rngs)
def __call__(self, x: jax.Array) -> jax.Array:
x = x + self.attn(self.norm1(x))
x = x + self.mlp(self.norm2(x))
return x
mod = ViTEncoderBlock(768, 3072, 12)
x = jnp.ones((4, 256, 768))
y = mod(x)
print(y.shape)
(4, 256, 768)
class ViT(nnx.Module):
"""
Vision Transformer (ViT) Feature Extractor, based on: "Dosovitskiy et al.,
An Image is Worth 16x16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale <https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11929>"
"""
def __init__(
self,
in_channels: int, # dimension of input channels
img_size: int, # dimension of input image
patch_size: int, # dimension of patch size
hidden_size: int = 768, # dimension of hidden layer
mlp_dim: int = 3072, # dimension of feedforward layer
num_layers: int = 12, # number of transformer blocks
num_heads: int = 12, # number of attention heads
dropout_rate: float = 0.0,
*,
rngs: nnx.Rngs = nnx.Rngs(0),
):
if hidden_size % num_heads != 0:
raise ValueError("hidden_size should be divisible by num_heads.")
self.patch_embedding = PatchEmbeddingBlock(
in_channels=in_channels,
img_size=img_size,
patch_size=patch_size,
hidden_size=hidden_size,
dropout_rate=dropout_rate,
rngs=rngs,
)
self.blocks = [
ViTEncoderBlock(hidden_size, mlp_dim, num_heads, dropout_rate, rngs=rngs)
for i in range(num_layers)
]
self.norm = nnx.LayerNorm(hidden_size, rngs=rngs)
def __call__(self, x: jax.Array) -> jax.Array:
x = self.patch_embedding(x)
hidden_states_out = []
for blk in self.blocks:
x = blk(x)
hidden_states_out.append(x)
x = self.norm(x)
return x, hidden_states_out
mod = ViT(3, 224, 16)
x = jnp.ones((4, 224, 224, 3))
y, hstates = mod(x)
print(y.shape, [s.shape for s in hstates])
(4, 196, 768) [(4, 196, 768), (4, 196, 768), (4, 196, 768), (4, 196, 768), (4, 196, 768), (4, 196, 768), (4, 196, 768), (4, 196, 768), (4, 196, 768), (4, 196, 768), (4, 196, 768), (4, 196, 768)]
At this point we implemented the encoder of the UNETR model. As we can see from the above output, ViT provides one encoded feature map and a list of intermediate feature maps. Three of them will be used in the decoding part.
UNETR blocks implementation#
Now, we can implement remaining blocks and assemble them together in the UNETR implementation
Below, we will implement the following modules:
UNETRUnetrBasicBlock: creates the first skip connection from the input.UnetResBlock
UnetrPrUpBlock: projection upsampling modules to create skip connections from the intermediate feature maps provided by ViT.UnetrUpBlock: upsampling modules used in the decoder
class Conv2dNormActivation(nnx.Sequential):
def __init__(
self,
in_channels: int,
out_channels: int,
kernel_size: int = 3,
stride: int = 1,
padding: int | None = None,
groups: int = 1,
norm_layer: Callable[..., nnx.Module] = nnx.BatchNorm,
activation_layer: Callable = nnx.relu,
dilation: int = 1,
bias: bool | None = None,
rngs: nnx.Rngs = nnx.Rngs(0),
):
self.out_channels = out_channels
if padding is None:
padding = (kernel_size - 1) // 2 * dilation
if bias is None:
bias = norm_layer is None
# sequence integer pairs that give the padding to apply before
# and after each spatial dimension
padding = ((padding, padding), (padding, padding))
layers = [
nnx.Conv(
in_channels,
out_channels,
kernel_size=(kernel_size, kernel_size),
strides=(stride, stride),
padding=padding,
kernel_dilation=(dilation, dilation),
feature_group_count=groups,
use_bias=bias,
rngs=rngs,
)
]
if norm_layer is not None:
layers.append(norm_layer(out_channels, rngs=rngs))
if activation_layer is not None:
layers.append(activation_layer)
super().__init__(*layers)
class InstanceNorm(nnx.GroupNorm):
def __init__(self, num_features, **kwargs):
num_groups, group_size = num_features, None
super().__init__(
num_features,
num_groups=num_groups,
group_size=group_size,
**kwargs,
)
class UnetResBlock(nnx.Module):
def __init__(
self,
in_channels: int,
out_channels: int,
kernel_size: int,
stride: int,
norm_layer: Callable[..., nnx.Module] = InstanceNorm,
activation_layer: Callable = nnx.leaky_relu,
*,
rngs: nnx.Rngs = nnx.Rngs(0),
):
self.conv_norm_act1 = Conv2dNormActivation(
in_channels=in_channels,
out_channels=out_channels,
kernel_size=kernel_size,
stride=stride,
norm_layer=norm_layer,
activation_layer=activation_layer,
rngs=rngs,
)
self.conv_norm2 = Conv2dNormActivation(
in_channels=out_channels,
out_channels=out_channels,
kernel_size=kernel_size,
stride=1,
norm_layer=norm_layer,
activation_layer=None,
rngs=rngs,
)
self.downsample = (in_channels != out_channels) or (stride != 1)
if self.downsample:
self.conv_norm3 = Conv2dNormActivation(
in_channels=in_channels,
out_channels=out_channels,
kernel_size=1,
stride=stride,
norm_layer=norm_layer,
activation_layer=None,
rngs=rngs,
)
self.act = activation_layer
def __call__(self, x: jax.Array) -> jax.Array:
residual = x
out = self.conv_norm_act1(x)
out = self.conv_norm2(out)
if self.downsample:
residual = self.conv_norm3(residual)
out += residual
out = self.act(out)
return out
mod = UnetResBlock(16, 32, 3, 1)
x = jnp.ones((4, 24, 24, 16))
y = mod(x)
print(y.shape)
(4, 24, 24, 32)
class UnetrBasicBlock(nnx.Module):
def __init__(
self,
in_channels: int,
out_channels: int,
kernel_size: int,
stride: int,
norm_layer: Callable[..., nnx.Module] = InstanceNorm,
*,
rngs: nnx.Rngs = nnx.Rngs(0),
):
self.layer = UnetResBlock(
in_channels=in_channels,
out_channels=out_channels,
kernel_size=kernel_size,
stride=stride,
norm_layer=norm_layer,
)
def __call__(self, x: jax.Array) -> jax.Array:
return self.layer(x)
mod = UnetrBasicBlock(16, 32, 3, 1)
x = jnp.ones((4, 24, 24, 16))
y = mod(x)
print(y.shape)
(4, 24, 24, 32)
class UnetrPrUpBlock(nnx.Module):
"""
A projection upsampling module for UNETR: "Hatamizadeh et al.,
UNETR: Transformers for 3D Medical Image Segmentation <https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.10504>"
"""
def __init__(
self,
in_channels: int, # number of input channels.
out_channels: int, # number of output channels.
num_layer: int, # number of upsampling blocks.
kernel_size: int,
stride: int,
upsample_kernel_size: int = 2, # convolution kernel size for transposed convolution layers.
norm_layer: Callable[..., nnx.Module] = InstanceNorm,
*,
rngs: nnx.Rngs = nnx.Rngs(0),
):
upsample_stride = upsample_kernel_size
self.transp_conv_init = nnx.ConvTranspose(
in_features=in_channels,
out_features=out_channels,
kernel_size=(upsample_kernel_size, upsample_kernel_size),
strides=(upsample_stride, upsample_stride),
padding="VALID",
rngs=rngs,
)
self.blocks = [
nnx.Sequential(
nnx.ConvTranspose(
in_features=out_channels,
out_features=out_channels,
kernel_size=(upsample_kernel_size, upsample_kernel_size),
strides=(upsample_stride, upsample_stride),
rngs=rngs,
),
UnetResBlock(
in_channels=out_channels,
out_channels=out_channels,
kernel_size=kernel_size,
stride=stride,
norm_layer=norm_layer,
rngs=rngs,
),
)
for i in range(num_layer)
]
def __call__(self, x: jax.Array) -> jax.Array:
x = self.transp_conv_init(x)
for blk in self.blocks:
x = blk(x)
return x
mod = UnetrPrUpBlock(16, 32, 2, 3, 1)
x = jnp.ones((4, 24, 24, 16))
y = mod(x)
print(y.shape)
(4, 192, 192, 32)
class UnetrUpBlock(nnx.Module):
"""
An upsampling module for UNETR: "Hatamizadeh et al.,
UNETR: Transformers for 3D Medical Image Segmentation <https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.10504>"
"""
def __init__(
self,
in_channels: int,
out_channels: int,
kernel_size: int,
upsample_kernel_size: int = 2, # convolution kernel size for transposed convolution layers.
norm_layer: Callable[..., nnx.Module] = InstanceNorm,
*,
rngs: nnx.Rngs = nnx.Rngs(0),
) -> None:
upsample_stride = upsample_kernel_size
self.transp_conv = nnx.ConvTranspose(
in_features=in_channels,
out_features=out_channels,
kernel_size=(upsample_kernel_size, upsample_kernel_size),
strides=(upsample_stride, upsample_stride),
padding="VALID",
rngs=rngs,
)
self.conv_block = UnetResBlock(
out_channels + out_channels,
out_channels,
kernel_size=kernel_size,
stride=1,
norm_layer=norm_layer,
rngs=rngs,
)
def __call__(self, x: jax.Array, skip: jax.Array) -> jax.Array:
out = self.transp_conv(x)
out = jnp.concat((out, skip), axis=-1)
out = self.conv_block(out)
return out
mod = UnetrUpBlock(16, 32, 3)
x = jnp.ones((4, 24, 24, 16))
skip = jnp.ones((4, 2 * 24, 2 * 24, 32))
y = mod(x, skip)
print(y.shape)
(4, 48, 48, 32)
class UNETR(nnx.Module):
"""UNETR model ported to NNX from MONAI implementation:
- https://github.com/Project-MONAI/MONAI/blob/dev/monai/networks/nets/unetr.py
"""
def __init__(
self,
out_channels: int,
in_channels: int = 3,
img_size: int = 256,
feature_size: int = 16,
hidden_size: int = 768,
mlp_dim: int = 3072,
num_heads: int = 12,
dropout_rate: float = 0.0,
norm_layer: Callable[..., nnx.Module] = InstanceNorm,
*,
rngs: nnx.Rngs = nnx.Rngs(0),
):
if hidden_size % num_heads != 0:
raise ValueError("hidden_size should be divisible by num_heads.")
self.num_layers = 12
self.patch_size = 16
self.feat_size = img_size // self.patch_size
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.vit = ViT(
in_channels=in_channels,
img_size=img_size,
patch_size=self.patch_size,
hidden_size=hidden_size,
mlp_dim=mlp_dim,
num_layers=self.num_layers,
num_heads=num_heads,
dropout_rate=dropout_rate,
rngs=rngs,
)
self.encoder1 = UnetrBasicBlock(
in_channels=in_channels,
out_channels=feature_size,
kernel_size=3,
stride=1,
norm_layer=norm_layer,
rngs=rngs,
)
self.encoder2 = UnetrPrUpBlock(
in_channels=hidden_size,
out_channels=feature_size * 2,
num_layer=2,
kernel_size=3,
stride=1,
upsample_kernel_size=2,
norm_layer=norm_layer,
rngs=rngs,
)
self.encoder3 = UnetrPrUpBlock(
in_channels=hidden_size,
out_channels=feature_size * 4,
num_layer=1,
kernel_size=3,
stride=1,
upsample_kernel_size=2,
norm_layer=norm_layer,
rngs=rngs,
)
self.encoder4 = UnetrPrUpBlock(
in_channels=hidden_size,
out_channels=feature_size * 8,
num_layer=0,
kernel_size=3,
stride=1,
upsample_kernel_size=2,
norm_layer=norm_layer,
rngs=rngs,
)
self.decoder5 = UnetrUpBlock(
in_channels=hidden_size,
out_channels=feature_size * 8,
kernel_size=3,
upsample_kernel_size=2,
norm_layer=norm_layer,
rngs=rngs,
)
self.decoder4 = UnetrUpBlock(
in_channels=feature_size * 8,
out_channels=feature_size * 4,
kernel_size=3,
upsample_kernel_size=2,
norm_layer=norm_layer,
rngs=rngs,
)
self.decoder3 = UnetrUpBlock(
in_channels=feature_size * 4,
out_channels=feature_size * 2,
kernel_size=3,
upsample_kernel_size=2,
norm_layer=norm_layer,
rngs=rngs,
)
self.decoder2 = UnetrUpBlock(
in_channels=feature_size * 2,
out_channels=feature_size,
kernel_size=3,
upsample_kernel_size=2,
norm_layer=norm_layer,
rngs=rngs,
)
self.out = nnx.Conv(
in_features=feature_size,
out_features=out_channels,
kernel_size=(1, 1),
strides=(1, 1),
padding="VALID",
use_bias=True,
rngs=rngs,
)
self.proj_axes = (0, 1, 2, 3)
self.proj_view_shape = [self.feat_size, self.feat_size, self.hidden_size]
def proj_feat(self, x: jax.Array) -> jax.Array:
new_view = [x.shape[0]] + self.proj_view_shape
x = x.reshape(new_view)
x = jnp.permute_dims(x, self.proj_axes)
return x
def __call__(self, x_in: jax.Array) -> jax.Array:
x, hidden_states_out = self.vit(x_in)
enc1 = self.encoder1(x_in)
x2 = hidden_states_out[3]
enc2 = self.encoder2(self.proj_feat(x2))
x3 = hidden_states_out[6]
enc3 = self.encoder3(self.proj_feat(x3))
x4 = hidden_states_out[9]
enc4 = self.encoder4(self.proj_feat(x4))
dec4 = self.proj_feat(x)
dec3 = self.decoder5(dec4, enc4)
dec2 = self.decoder4(dec3, enc3)
dec1 = self.decoder3(dec2, enc2)
out = self.decoder2(dec1, enc1)
return self.out(out)
# We'll use a different number of heads to make a smaller model
model = UNETR(out_channels=3, num_heads=4)
x = jnp.ones((4, 256, 256, 3))
y = model(x)
print(y.shape)
(4, 256, 256, 3)
We can visualize and inspect the architecture on the implemented model using nnx.display(model).
Train the model#
In previous sections we defined training and validation dataloaders and the model. In this section we will train the model and define the loss function and the optimizer to perform the parameters optimization.
For the semantic segmentation task, we can define the loss function as a sum of Cross-Entropy and Jaccard loss functions. The Cross-Entropy loss function is a standard loss function for a multi-class classification tasks and the Jaccard loss function helps directly optimizing Intersection-over-Union measure for semantic segmentation.
import optax
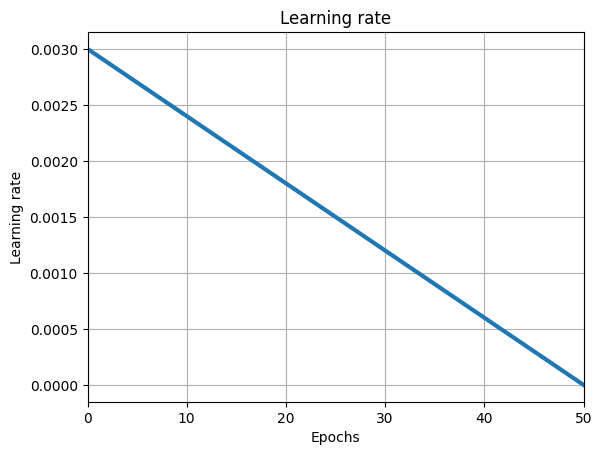
num_epochs = 50
total_steps = len(train_dataset) // train_batch_size
learning_rate = 0.003
momentum = 0.9
lr_schedule = optax.linear_schedule(learning_rate, 0.0, num_epochs * total_steps)
iterate_subsample = np.linspace(0, num_epochs * total_steps, 100)
plt.plot(
np.linspace(0, num_epochs, len(iterate_subsample)),
[lr_schedule(i) for i in iterate_subsample],
lw=3,
)
plt.title("Learning rate")
plt.xlabel("Epochs")
plt.ylabel("Learning rate")
plt.grid()
plt.xlim((0, num_epochs))
plt.show()
optimizer = nnx.Optimizer(model, optax.adam(lr_schedule, momentum))
Let us implement Jaccard loss and the loss function combining Cross-Entropy and Jaccard losses.
def compute_softmax_jaccard_loss(logits, masks, reduction="mean"):
assert reduction in ("mean", "sum")
y_pred = nnx.softmax(logits, axis=-1)
b, c = y_pred.shape[0], y_pred.shape[-1]
y = nnx.one_hot(masks, num_classes=c, axis=-1)
y_pred = y_pred.reshape((b, -1, c))
y = y.reshape((b, -1, c))
intersection = y_pred * y
union = y_pred + y - intersection + 1e-8
intersection = jnp.sum(intersection, axis=1)
union = jnp.sum(union, axis=1)
if reduction == "mean":
intersection = jnp.mean(intersection)
union = jnp.mean(union)
elif reduction == "sum":
intersection = jnp.sum(intersection)
union = jnp.sum(union)
return 1.0 - intersection / union
def compute_losses_and_logits(model: nnx.Module, images: jax.Array, masks: jax.Array):
logits = model(images)
xentropy_loss = optax.softmax_cross_entropy_with_integer_labels(
logits=logits, labels=masks
).mean()
jacc_loss = compute_softmax_jaccard_loss(logits=logits, masks=masks)
loss = xentropy_loss + jacc_loss
return loss, (xentropy_loss, jacc_loss, logits)
Now, we will implement a confusion matrix metric derived from nnx.Metric. A confusion matrix will help us to compute the Intersection-Over-Union (IoU) metric per class and on average. Finally, we can also compute the accuracy metric using the confusion matrix.
class ConfusionMatrix(nnx.Metric):
def __init__(
self,
num_classes: int,
average: str | None = None,
):
assert average in (None, "samples", "recall", "precision")
assert num_classes > 0
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.average = average
self.confusion_matrix = nnx.metrics.MetricState(
jnp.zeros((self.num_classes, self.num_classes), dtype=jnp.int32)
)
self.count = nnx.metrics.MetricState(jnp.array(0, dtype=jnp.int32))
def reset(self):
self.confusion_matrix.value = jnp.zeros((self.num_classes, self.num_classes), dtype=jnp.int32)
self.count.value = jnp.array(0, dtype=jnp.int32)
def _check_shape(self, y_pred: jax.Array, y: jax.Array):
if y_pred.shape[-1] != self.num_classes:
raise ValueError(f"y_pred does not have correct number of classes: {y_pred.shape[-1]} vs {self.num_classes}")
if not (y.ndim + 1 == y_pred.ndim):
raise ValueError(
f"y_pred must have shape (batch_size, num_classes (currently set to {self.num_classes}), ...) "
"and y must have shape of (batch_size, ...), "
f"but given {y.shape} vs {y_pred.shape}."
)
def update(self, **kwargs):
# We assume that y.max() < self.num_classes and y.min() >= 0
assert "y" in kwargs
assert "y_pred" in kwargs
y_pred = kwargs["y_pred"]
y = kwargs["y"]
self._check_shape(y_pred, y)
self.count.value += y_pred.shape[0]
y_pred = jnp.argmax(y_pred, axis=-1).ravel()
y = y.ravel()
indices = self.num_classes * y + y_pred
matrix = jnp.bincount(indices, minlength=self.num_classes**2, length=self.num_classes**2)
matrix = matrix.reshape((self.num_classes, self.num_classes))
self.confusion_matrix.value += matrix
def compute(self) -> jax.Array:
if self.average:
confusion_matrix = self.confusion_matrix.value.astype("float")
if self.average == "samples":
return confusion_matrix / self.count.value
else:
return self.normalize(self.confusion_matrix.value, self.average)
return self.confusion_matrix.value
@staticmethod
def normalize(matrix: jax.Array, average: str) -> jax.Array:
"""Normalize given `matrix` with given `average`."""
if average == "recall":
return matrix / (jnp.expand_dims(matrix.sum(axis=1), axis=1) + 1e-15)
elif average == "precision":
return matrix / (matrix.sum(axis=0) + 1e-15)
else:
raise ValueError("Argument average should be one of 'samples', 'recall', 'precision'")
def compute_iou(cm: jax.Array) -> jax.Array:
return jnp.diag(cm) / (cm.sum(axis=1) + cm.sum(axis=0) - jnp.diag(cm) + 1e-15)
def compute_mean_iou(cm: jax.Array) -> jax.Array:
return compute_iou(cm).mean()
def compute_accuracy(cm: jax.Array) -> jax.Array:
return jnp.diag(cm).sum() / (cm.sum() + 1e-15)
Next, let’s define training and evaluation steps:
@nnx.jit
def train_step(
model: nnx.Module, optimizer: nnx.Optimizer, batch: dict[str, np.ndarray]
):
# Convert numpy arrays to jax.Array on GPU
images = jnp.array(batch["image"])
masks = jnp.array(batch["mask"], dtype=jnp.int32)
grad_fn = nnx.value_and_grad(compute_losses_and_logits, has_aux=True)
(loss, (xentropy_loss, jacc_loss, logits)), grads = grad_fn(model, images, masks)
optimizer.update(grads) # In-place updates.
return loss, xentropy_loss, jacc_loss
@nnx.jit
def eval_step(
model: nnx.Module, batch: dict[str, np.ndarray], eval_metrics: nnx.MultiMetric
):
# Convert numpy arrays to jax.Array on GPU
images = jnp.array(batch["image"])
masks = jnp.array(batch["mask"], dtype=jnp.int32)
loss, (_, _, logits) = compute_losses_and_logits(model, images, masks)
eval_metrics.update(
total_loss=loss,
y_pred=logits,
y=masks,
) # In-place updates.
We will also define metrics we want to compute during the evaluation phase: total loss and confusion matrix computed on training and validation datasets. Finally, we define helper objects to store the metrics history. Metrics like IoU per class, mean IoU and accuracy will be computed using the confusion matrix in the evaluation code.
eval_metrics = nnx.MultiMetric(
total_loss=nnx.metrics.Average('total_loss'),
confusion_matrix=ConfusionMatrix(num_classes=3),
)
eval_metrics_history = {
"train_total_loss": [],
"train_IoU": [],
"train_mean_IoU": [],
"train_accuracy": [],
"val_total_loss": [],
"val_IoU": [],
"val_mean_IoU": [],
"val_accuracy": [],
}
Let us define the training and evaluation logic. We define as well a checkpoint manager to store two best models defined by validation mean IoU metric value.
import time
import orbax.checkpoint as ocp
def train_one_epoch(epoch):
start_time = time.time()
model.train() # Set model to the training mode: e.g. update batch statistics
for step, batch in enumerate(train_loader):
total_loss, xentropy_loss, jaccard_loss = train_step(model, optimizer, batch)
print(
f"\r[train] epoch: {epoch + 1}/{num_epochs}, iteration: {step}/{total_steps}, "
f"total loss: {total_loss.item():.4f} ",
f"xentropy loss: {xentropy_loss.item():.4f} ",
f"jaccard loss: {jaccard_loss.item():.4f} ",
end="")
print("\r", end="")
elapsed = time.time() - start_time
print(
f"\n[train] epoch: {epoch + 1}/{num_epochs}, elapsed time: {elapsed:.2f} seconds"
)
def evaluate_model(epoch):
start_time = time.time()
# Compute the metrics on the train and val sets after each training epoch.
model.eval() # Set model to evaluation model: e.g. use stored batch statistics
for tag, eval_loader in [("train", train_eval_loader), ("val", val_loader)]:
eval_metrics.reset() # Reset the eval metrics
for val_batch in eval_loader:
eval_step(model, val_batch, eval_metrics)
for metric, value in eval_metrics.compute().items():
if metric == "confusion_matrix":
eval_metrics_history[f"{tag}_IoU"].append(
compute_iou(value)
)
eval_metrics_history[f"{tag}_mean_IoU"].append(
compute_mean_iou(value)
)
eval_metrics_history[f"{tag}_accuracy"].append(
compute_accuracy(value)
)
else:
eval_metrics_history[f'{tag}_{metric}'].append(value)
print(
f"[{tag}] epoch: {epoch + 1}/{num_epochs} "
f"\n - total loss: {eval_metrics_history[f'{tag}_total_loss'][-1]:0.4f} "
f"\n - IoU per class: {eval_metrics_history[f'{tag}_IoU'][-1].tolist()} "
f"\n - Mean IoU: {eval_metrics_history[f'{tag}_mean_IoU'][-1]:0.4f} "
f"\n - Accuracy: {eval_metrics_history[f'{tag}_accuracy'][-1]:0.4f} "
"\n"
)
elapsed = time.time() - start_time
print(
f"[evaluation] epoch: {epoch + 1}/{num_epochs}, elapsed time: {elapsed:.2f} seconds"
)
return eval_metrics_history['val_mean_IoU'][-1]
path = ocp.test_utils.erase_and_create_empty("/tmp/output-oxford-model/")
options = ocp.CheckpointManagerOptions(max_to_keep=2)
mngr = ocp.CheckpointManager(path, options=options)
def save_model(epoch):
state = nnx.state(model)
# We should convert PRNGKeyArray to the old format for Dropout layers
# https://github.com/google/flax/issues/4231
def get_key_data(x):
if isinstance(x, jax._src.prng.PRNGKeyArray):
if isinstance(x.dtype, jax._src.prng.KeyTy):
return jax.random.key_data(x)
return x
serializable_state = jax.tree.map(get_key_data, state)
mngr.save(epoch, args=ocp.args.StandardSave(serializable_state))
mngr.wait_until_finished()
Now we can start the training. It can take around 45 minutes using a single GPU and use 19GB of GPU memory.
%%time
best_val_mean_iou = 0.0
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
train_one_epoch(epoch)
if (epoch % 3 == 0) or (epoch == num_epochs - 1):
val_mean_iou = evaluate_model(epoch)
if val_mean_iou > best_val_mean_iou:
save_model(epoch)
best_val_mean_iou = val_mean_iou
[train] epoch: 1/50, iteration: 67/71, total loss: 1.5128 xentropy loss: 0.8543 jaccard loss: 0.6585
[train] epoch: 1/50, elapsed time: 98.28 seconds
[train] epoch: 1/50
- total loss: 1.4808
- IoU per class: [0.3311152458190918, 0.5875526070594788, 0.07520102709531784]
- Mean IoU: 0.3313
- Accuracy: 0.6198
[val] epoch: 1/50
- total loss: 1.4837
- IoU per class: [0.32379695773124695, 0.5863257050514221, 0.07609017938375473]
- Mean IoU: 0.3287
- Accuracy: 0.6174
[evaluation] epoch: 1/50, elapsed time: 95.73 seconds
[train] epoch: 2/50, iteration: 67/71, total loss: 1.4376 xentropy loss: 0.8077 jaccard loss: 0.6299
[train] epoch: 2/50, elapsed time: 42.02 seconds
[train] epoch: 3/50, iteration: 67/71, total loss: 1.3881 xentropy loss: 0.7764 jaccard loss: 0.6118
[train] epoch: 3/50, elapsed time: 42.77 seconds
[train] epoch: 4/50, iteration: 67/71, total loss: 1.3697 xentropy loss: 0.7662 jaccard loss: 0.6035
[train] epoch: 4/50, elapsed time: 42.69 seconds
[train] epoch: 4/50
- total loss: 1.3479
- IoU per class: [0.4200800955295563, 0.6404442191123962, 0.10423737019300461]
- Mean IoU: 0.3883
- Accuracy: 0.6735
[val] epoch: 4/50
- total loss: 1.3526
- IoU per class: [0.4134039580821991, 0.6370245814323425, 0.10554961115121841]
- Mean IoU: 0.3853
- Accuracy: 0.6700
[evaluation] epoch: 4/50, elapsed time: 18.13 seconds
[train] epoch: 5/50, iteration: 67/71, total loss: 1.3223 xentropy loss: 0.7382 jaccard loss: 0.5841
[train] epoch: 5/50, elapsed time: 42.68 seconds
[train] epoch: 6/50, iteration: 67/71, total loss: 1.2856 xentropy loss: 0.7155 jaccard loss: 0.5701
[train] epoch: 6/50, elapsed time: 41.52 seconds
[train] epoch: 7/50, iteration: 67/71, total loss: 1.2704 xentropy loss: 0.7096 jaccard loss: 0.5608
[train] epoch: 7/50, elapsed time: 41.99 seconds
[train] epoch: 7/50
- total loss: 1.2590
- IoU per class: [0.4778529703617096, 0.6718385815620422, 0.12118919938802719]
- Mean IoU: 0.4236
- Accuracy: 0.7051
[val] epoch: 7/50
- total loss: 1.2703
- IoU per class: [0.46884578466415405, 0.6662946939468384, 0.12407345324754715]
- Mean IoU: 0.4197
- Accuracy: 0.7002
[evaluation] epoch: 7/50, elapsed time: 18.11 seconds
[train] epoch: 8/50, iteration: 67/71, total loss: 1.2547 xentropy loss: 0.7002 jaccard loss: 0.5545
[train] epoch: 8/50, elapsed time: 41.78 seconds
[train] epoch: 9/50, iteration: 67/71, total loss: 1.2426 xentropy loss: 0.6930 jaccard loss: 0.5496
[train] epoch: 9/50, elapsed time: 41.77 seconds
[train] epoch: 10/50, iteration: 67/71, total loss: 1.2336 xentropy loss: 0.6879 jaccard loss: 0.5456
[train] epoch: 10/50, elapsed time: 42.35 seconds
[train] epoch: 10/50
- total loss: 1.2209
- IoU per class: [0.49634286761283875, 0.6871868371963501, 0.14223484694957733]
- Mean IoU: 0.4419
- Accuracy: 0.7183
[val] epoch: 10/50
- total loss: 1.2344
- IoU per class: [0.4855667054653168, 0.6802844405174255, 0.14551958441734314]
- Mean IoU: 0.4371
- Accuracy: 0.7124
[evaluation] epoch: 10/50, elapsed time: 18.03 seconds
[train] epoch: 11/50, iteration: 67/71, total loss: 1.2336 xentropy loss: 0.6888 jaccard loss: 0.5448
[train] epoch: 11/50, elapsed time: 42.32 seconds
[train] epoch: 12/50, iteration: 67/71, total loss: 1.2240 xentropy loss: 0.6831 jaccard loss: 0.5410
[train] epoch: 12/50, elapsed time: 42.16 seconds
[train] epoch: 13/50, iteration: 67/71, total loss: 1.2192 xentropy loss: 0.6807 jaccard loss: 0.5384
[train] epoch: 13/50, elapsed time: 42.99 seconds
[train] epoch: 13/50
- total loss: 1.2033
- IoU per class: [0.5088780522346497, 0.6932766437530518, 0.14735452830791473]
- Mean IoU: 0.4498
- Accuracy: 0.7244
[val] epoch: 13/50
- total loss: 1.2176
- IoU per class: [0.49794140458106995, 0.6858826875686646, 0.15074597299098969]
- Mean IoU: 0.4449
- Accuracy: 0.7182
[evaluation] epoch: 13/50, elapsed time: 18.08 seconds
[train] epoch: 14/50, iteration: 67/71, total loss: 1.2125 xentropy loss: 0.6757 jaccard loss: 0.5367
[train] epoch: 14/50, elapsed time: 41.59 seconds
[train] epoch: 15/50, iteration: 67/71, total loss: 1.2067 xentropy loss: 0.6716 jaccard loss: 0.5350
[train] epoch: 15/50, elapsed time: 42.94 seconds
[train] epoch: 16/50, iteration: 67/71, total loss: 1.2003 xentropy loss: 0.6670 jaccard loss: 0.5333
[train] epoch: 16/50, elapsed time: 42.27 seconds
[train] epoch: 16/50
- total loss: 1.1923
- IoU per class: [0.5148026943206787, 0.697281002998352, 0.15585048496723175]
- Mean IoU: 0.4560
- Accuracy: 0.7282
[val] epoch: 16/50
- total loss: 1.2069
- IoU per class: [0.5041127800941467, 0.6899872422218323, 0.15917228162288666]
- Mean IoU: 0.4511
- Accuracy: 0.7221
[evaluation] epoch: 16/50, elapsed time: 17.95 seconds
[train] epoch: 17/50, iteration: 67/71, total loss: 1.2013 xentropy loss: 0.6684 jaccard loss: 0.5330
[train] epoch: 17/50, elapsed time: 42.13 seconds
[train] epoch: 18/50, iteration: 67/71, total loss: 1.1990 xentropy loss: 0.6673 jaccard loss: 0.5317
[train] epoch: 18/50, elapsed time: 42.59 seconds
[train] epoch: 19/50, iteration: 67/71, total loss: 1.1928 xentropy loss: 0.6651 jaccard loss: 0.5277
[train] epoch: 19/50, elapsed time: 42.52 seconds
[train] epoch: 19/50
- total loss: 1.1801
- IoU per class: [0.5213924646377563, 0.7013189792633057, 0.1597258597612381]
- Mean IoU: 0.4608
- Accuracy: 0.7320
[val] epoch: 19/50
- total loss: 1.1945
- IoU per class: [0.5107904672622681, 0.6942348480224609, 0.1630152016878128]
- Mean IoU: 0.4560
- Accuracy: 0.7261
[evaluation] epoch: 19/50, elapsed time: 18.10 seconds
[train] epoch: 20/50, iteration: 67/71, total loss: 1.1808 xentropy loss: 0.6580 jaccard loss: 0.5228
[train] epoch: 20/50, elapsed time: 42.61 seconds
[train] epoch: 21/50, iteration: 67/71, total loss: 1.1872 xentropy loss: 0.6665 jaccard loss: 0.5207
[train] epoch: 21/50, elapsed time: 41.39 seconds
[train] epoch: 22/50, iteration: 67/71, total loss: 1.1753 xentropy loss: 0.6563 jaccard loss: 0.5190
[train] epoch: 22/50, elapsed time: 42.60 seconds
[train] epoch: 22/50
- total loss: 1.1565
- IoU per class: [0.5349406003952026, 0.7107416987419128, 0.1611461639404297]
- Mean IoU: 0.4689
- Accuracy: 0.7396
[val] epoch: 22/50
- total loss: 1.1714
- IoU per class: [0.5250519514083862, 0.7039015889167786, 0.16501173377037048]
- Mean IoU: 0.4647
- Accuracy: 0.7341
[evaluation] epoch: 22/50, elapsed time: 18.11 seconds
[train] epoch: 23/50, iteration: 67/71, total loss: 1.1682 xentropy loss: 0.6515 jaccard loss: 0.5166
[train] epoch: 23/50, elapsed time: 42.13 seconds
[train] epoch: 24/50, iteration: 67/71, total loss: 1.1598 xentropy loss: 0.6455 jaccard loss: 0.5142
[train] epoch: 24/50, elapsed time: 42.78 seconds
[train] epoch: 25/50, iteration: 67/71, total loss: 1.1578 xentropy loss: 0.6439 jaccard loss: 0.5138
[train] epoch: 25/50, elapsed time: 41.81 seconds
[train] epoch: 25/50
- total loss: 1.1493
- IoU per class: [0.5394869446754456, 0.714061975479126, 0.16233977675437927]
- Mean IoU: 0.4720
- Accuracy: 0.7427
[val] epoch: 25/50
- total loss: 1.1646
- IoU per class: [0.5292088389396667, 0.7074748277664185, 0.1662358045578003]
- Mean IoU: 0.4676
- Accuracy: 0.7373
[evaluation] epoch: 25/50, elapsed time: 18.03 seconds
[train] epoch: 26/50, iteration: 67/71, total loss: 1.1541 xentropy loss: 0.6419 jaccard loss: 0.5121
[train] epoch: 26/50, elapsed time: 42.32 seconds
[train] epoch: 27/50, iteration: 67/71, total loss: 1.1530 xentropy loss: 0.6423 jaccard loss: 0.5107
[train] epoch: 27/50, elapsed time: 43.11 seconds
[train] epoch: 28/50, iteration: 67/71, total loss: 1.1454 xentropy loss: 0.6403 jaccard loss: 0.5050
[train] epoch: 28/50, elapsed time: 42.75 seconds
[train] epoch: 28/50
- total loss: 1.1361
- IoU per class: [0.5401146411895752, 0.7192343473434448, 0.17713244259357452]
- Mean IoU: 0.4788
- Accuracy: 0.7459
[val] epoch: 28/50
- total loss: 1.1509
- IoU per class: [0.5303367972373962, 0.713244616985321, 0.1806260049343109]
- Mean IoU: 0.4747
- Accuracy: 0.7409
[evaluation] epoch: 28/50, elapsed time: 18.15 seconds
[train] epoch: 29/50, iteration: 67/71, total loss: 1.1461 xentropy loss: 0.6397 jaccard loss: 0.5063
[train] epoch: 29/50, elapsed time: 41.27 seconds
[train] epoch: 30/50, iteration: 67/71, total loss: 1.1441 xentropy loss: 0.6386 jaccard loss: 0.5054
[train] epoch: 30/50, elapsed time: 43.06 seconds
[train] epoch: 31/50, iteration: 67/71, total loss: 1.1406 xentropy loss: 0.6385 jaccard loss: 0.5021
[train] epoch: 31/50, elapsed time: 42.35 seconds
[train] epoch: 31/50
- total loss: 1.1221
- IoU per class: [0.5476018190383911, 0.7231868505477905, 0.1709066480398178]
- Mean IoU: 0.4806
- Accuracy: 0.7496
[val] epoch: 31/50
- total loss: 1.1382
- IoU per class: [0.5371024012565613, 0.7168474793434143, 0.17449183762073517]
- Mean IoU: 0.4761
- Accuracy: 0.7444
[evaluation] epoch: 31/50, elapsed time: 18.18 seconds
[train] epoch: 32/50, iteration: 67/71, total loss: 1.1407 xentropy loss: 0.6383 jaccard loss: 0.5024
[train] epoch: 32/50, elapsed time: 42.78 seconds
[train] epoch: 33/50, iteration: 67/71, total loss: 1.1362 xentropy loss: 0.6381 jaccard loss: 0.4981
[train] epoch: 33/50, elapsed time: 42.83 seconds
[train] epoch: 34/50, iteration: 67/71, total loss: 1.1327 xentropy loss: 0.6366 jaccard loss: 0.4961
[train] epoch: 34/50, elapsed time: 42.60 seconds
[train] epoch: 34/50
- total loss: 1.0938
- IoU per class: [0.5674961805343628, 0.735647976398468, 0.1631506383419037]
- Mean IoU: 0.4888
- Accuracy: 0.7596
[val] epoch: 34/50
- total loss: 1.1083
- IoU per class: [0.5587170720100403, 0.7299370765686035, 0.16656328737735748]
- Mean IoU: 0.4851
- Accuracy: 0.7551
[evaluation] epoch: 34/50, elapsed time: 17.95 seconds
[train] epoch: 35/50, iteration: 67/71, total loss: 1.1244 xentropy loss: 0.6319 jaccard loss: 0.4925
[train] epoch: 35/50, elapsed time: 42.43 seconds
[train] epoch: 36/50, iteration: 67/71, total loss: 1.1275 xentropy loss: 0.6359 jaccard loss: 0.4916
[train] epoch: 36/50, elapsed time: 42.50 seconds
[train] epoch: 37/50, iteration: 67/71, total loss: 1.1254 xentropy loss: 0.6342 jaccard loss: 0.4912
[train] epoch: 37/50, elapsed time: 42.97 seconds
[train] epoch: 37/50
- total loss: 1.0758
- IoU per class: [0.5775947570800781, 0.7411153316497803, 0.1559378057718277]
- Mean IoU: 0.4915
- Accuracy: 0.7648
[val] epoch: 37/50
- total loss: 1.0889
- IoU per class: [0.5697115063667297, 0.736099123954773, 0.15949904918670654]
- Mean IoU: 0.4884
- Accuracy: 0.7609
[evaluation] epoch: 37/50, elapsed time: 18.29 seconds
[train] epoch: 38/50, iteration: 67/71, total loss: 1.1135 xentropy loss: 0.6283 jaccard loss: 0.4852
[train] epoch: 38/50, elapsed time: 42.40 seconds
[train] epoch: 39/50, iteration: 67/71, total loss: 1.1064 xentropy loss: 0.6222 jaccard loss: 0.4842
[train] epoch: 39/50, elapsed time: 42.89 seconds
[train] epoch: 40/50, iteration: 67/71, total loss: 1.0981 xentropy loss: 0.6188 jaccard loss: 0.4792
[train] epoch: 40/50, elapsed time: 42.52 seconds
[train] epoch: 40/50
- total loss: 1.0575
- IoU per class: [0.5876496434211731, 0.7454202771186829, 0.1702071875333786]
- Mean IoU: 0.5011
- Accuracy: 0.7698
[val] epoch: 40/50
- total loss: 1.0745
- IoU per class: [0.5783292055130005, 0.7390925288200378, 0.17342697083950043]
- Mean IoU: 0.4969
- Accuracy: 0.7649
[evaluation] epoch: 40/50, elapsed time: 18.13 seconds
[train] epoch: 41/50, iteration: 67/71, total loss: 1.1015 xentropy loss: 0.6202 jaccard loss: 0.4812
[train] epoch: 41/50, elapsed time: 42.75 seconds
[train] epoch: 42/50, iteration: 67/71, total loss: 1.0933 xentropy loss: 0.6148 jaccard loss: 0.4785
[train] epoch: 42/50, elapsed time: 42.70 seconds
[train] epoch: 43/50, iteration: 67/71, total loss: 1.0860 xentropy loss: 0.6113 jaccard loss: 0.4748
[train] epoch: 43/50, elapsed time: 42.48 seconds
[train] epoch: 43/50
- total loss: 1.0466
- IoU per class: [0.5935679078102112, 0.7484169006347656, 0.17425251007080078]
- Mean IoU: 0.5054
- Accuracy: 0.7726
[val] epoch: 43/50
- total loss: 1.0649
- IoU per class: [0.5832134485244751, 0.7414273023605347, 0.17751547694206238]
- Mean IoU: 0.5007
- Accuracy: 0.7673
[evaluation] epoch: 43/50, elapsed time: 18.06 seconds
[train] epoch: 44/50, iteration: 67/71, total loss: 1.0858 xentropy loss: 0.6108 jaccard loss: 0.4751
[train] epoch: 44/50, elapsed time: 42.08 seconds
[train] epoch: 45/50, iteration: 67/71, total loss: 1.0846 xentropy loss: 0.6083 jaccard loss: 0.4763
[train] epoch: 45/50, elapsed time: 42.20 seconds
[train] epoch: 46/50, iteration: 67/71, total loss: 1.0811 xentropy loss: 0.6053 jaccard loss: 0.4759
[train] epoch: 46/50, elapsed time: 42.44 seconds
[train] epoch: 46/50
- total loss: 1.0358
- IoU per class: [0.5985013246536255, 0.7518817782402039, 0.18402163684368134]
- Mean IoU: 0.5115
- Accuracy: 0.7757
[val] epoch: 46/50
- total loss: 1.0532
- IoU per class: [0.5885671377182007, 0.7452569603919983, 0.18743924796581268]
- Mean IoU: 0.5071
- Accuracy: 0.7707
[evaluation] epoch: 46/50, elapsed time: 17.97 seconds
[train] epoch: 47/50, iteration: 67/71, total loss: 1.0795 xentropy loss: 0.6050 jaccard loss: 0.4746
[train] epoch: 47/50, elapsed time: 42.24 seconds
[train] epoch: 48/50, iteration: 67/71, total loss: 1.0812 xentropy loss: 0.6076 jaccard loss: 0.4736
[train] epoch: 48/50, elapsed time: 43.06 seconds
[train] epoch: 49/50, iteration: 67/71, total loss: 1.0755 xentropy loss: 0.6033 jaccard loss: 0.4722
[train] epoch: 49/50, elapsed time: 42.87 seconds
[train] epoch: 49/50
- total loss: 1.0339
- IoU per class: [0.6011808514595032, 0.7519543766975403, 0.18255695700645447]
- Mean IoU: 0.5119
- Accuracy: 0.7763
[val] epoch: 49/50
- total loss: 1.0526
- IoU per class: [0.5906183123588562, 0.7446607351303101, 0.18571272492408752]
- Mean IoU: 0.5070
- Accuracy: 0.7708
[evaluation] epoch: 49/50, elapsed time: 17.92 seconds
[train] epoch: 50/50, iteration: 67/71, total loss: 1.0746 xentropy loss: 0.6023 jaccard loss: 0.4723
[train] epoch: 50/50, elapsed time: 42.67 seconds
[train] epoch: 50/50
- total loss: 1.0333
- IoU per class: [0.6012441515922546, 0.7520167231559753, 0.18340939283370972]
- Mean IoU: 0.5122
- Accuracy: 0.7764
[val] epoch: 50/50
- total loss: 1.0529
- IoU per class: [0.5903779864311218, 0.7444505095481873, 0.18650034070014954]
- Mean IoU: 0.5071
- Accuracy: 0.7707
[evaluation] epoch: 50/50, elapsed time: 18.28 seconds
CPU times: user 21min 59s, sys: 2min 51s, total: 24min 51s
Wall time: 43min 44s
2024-11-19 15:13:28.682932: E external/xla/xla/service/slow_operation_alarm.cc:65] Trying algorithm eng28{k2=2,k3=0} for conv (f32[16,32,2,2]{3,2,1,0}, u8[0]{0}) custom-call(f32[16,72,256,256]{3,2,1,0}, f32[32,72,255,255]{3,2,1,0}), window={size=255x255 rhs_reversal=1x1}, dim_labels=bf01_oi01->bf01, custom_call_target="__cudnn$convForward", backend_config={"cudnn_conv_backend_config":{"activation_mode":"kNone","conv_result_scale":1,"leakyrelu_alpha":0,"side_input_scale":0},"force_earliest_schedule":false,"operation_queue_id":"0","wait_on_operation_queues":[]} is taking a while...
2024-11-19 15:13:29.105239: E external/xla/xla/service/slow_operation_alarm.cc:133] The operation took 1.422412472s
Trying algorithm eng28{k2=2,k3=0} for conv (f32[16,32,2,2]{3,2,1,0}, u8[0]{0}) custom-call(f32[16,72,256,256]{3,2,1,0}, f32[32,72,255,255]{3,2,1,0}), window={size=255x255 rhs_reversal=1x1}, dim_labels=bf01_oi01->bf01, custom_call_target="__cudnn$convForward", backend_config={"cudnn_conv_backend_config":{"activation_mode":"kNone","conv_result_scale":1,"leakyrelu_alpha":0,"side_input_scale":0},"force_earliest_schedule":false,"operation_queue_id":"0","wait_on_operation_queues":[]} is taking a while...
2024-11-19 15:13:30.105387: E external/xla/xla/service/slow_operation_alarm.cc:65] Trying algorithm eng0{} for conv (f32[16,32,2,2]{3,2,1,0}, u8[0]{0}) custom-call(f32[16,72,256,256]{3,2,1,0}, f32[32,72,255,255]{3,2,1,0}), window={size=255x255 rhs_reversal=1x1}, dim_labels=bf01_oi01->bf01, custom_call_target="__cudnn$convForward", backend_config={"cudnn_conv_backend_config":{"activation_mode":"kNone","conv_result_scale":1,"leakyrelu_alpha":0,"side_input_scale":0},"force_earliest_schedule":false,"operation_queue_id":"0","wait_on_operation_queues":[]} is taking a while...
2024-11-19 15:13:30.272493: E external/xla/xla/service/slow_operation_alarm.cc:133] The operation took 1.167207376s
Trying algorithm eng0{} for conv (f32[16,32,2,2]{3,2,1,0}, u8[0]{0}) custom-call(f32[16,72,256,256]{3,2,1,0}, f32[32,72,255,255]{3,2,1,0}), window={size=255x255 rhs_reversal=1x1}, dim_labels=bf01_oi01->bf01, custom_call_target="__cudnn$convForward", backend_config={"cudnn_conv_backend_config":{"activation_mode":"kNone","conv_result_scale":1,"leakyrelu_alpha":0,"side_input_scale":0},"force_earliest_schedule":false,"operation_queue_id":"0","wait_on_operation_queues":[]} is taking a while...
2024-11-19 15:13:31.272637: E external/xla/xla/service/slow_operation_alarm.cc:65] Trying algorithm eng28{k2=1,k3=0} for conv (f32[16,32,2,2]{3,2,1,0}, u8[0]{0}) custom-call(f32[16,72,256,256]{3,2,1,0}, f32[32,72,255,255]{3,2,1,0}), window={size=255x255 rhs_reversal=1x1}, dim_labels=bf01_oi01->bf01, custom_call_target="__cudnn$convForward", backend_config={"cudnn_conv_backend_config":{"activation_mode":"kNone","conv_result_scale":1,"leakyrelu_alpha":0,"side_input_scale":0},"force_earliest_schedule":false,"operation_queue_id":"0","wait_on_operation_queues":[]} is taking a while...
2024-11-19 15:13:31.597345: E external/xla/xla/service/slow_operation_alarm.cc:133] The operation took 1.324807429s
Trying algorithm eng28{k2=1,k3=0} for conv (f32[16,32,2,2]{3,2,1,0}, u8[0]{0}) custom-call(f32[16,72,256,256]{3,2,1,0}, f32[32,72,255,255]{3,2,1,0}), window={size=255x255 rhs_reversal=1x1}, dim_labels=bf01_oi01->bf01, custom_call_target="__cudnn$convForward", backend_config={"cudnn_conv_backend_config":{"activation_mode":"kNone","conv_result_scale":1,"leakyrelu_alpha":0,"side_input_scale":0},"force_earliest_schedule":false,"operation_queue_id":"0","wait_on_operation_queues":[]} is taking a while...
We can check the saved models:
!ls /tmp/output-oxford-model/
45 49
/opt/conda/lib/python3.11/pty.py:89: RuntimeWarning: os.fork() was called. os.fork() is incompatible with multithreaded code, and JAX is multithreaded, so this will likely lead to a deadlock.
pid, fd = os.forkpty()
and visualize collected metrics:
epochs = [i for i in range(num_epochs) if (i % 3 == 0) or (i == num_epochs - 1)]
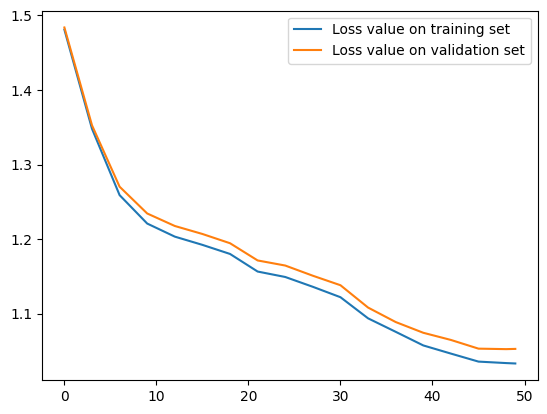
plt.plot(epochs, eval_metrics_history["train_total_loss"], label="Loss value on training set")
plt.plot(epochs, eval_metrics_history["val_total_loss"], label="Loss value on validation set")
plt.legend()
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7fb370eddfd0>
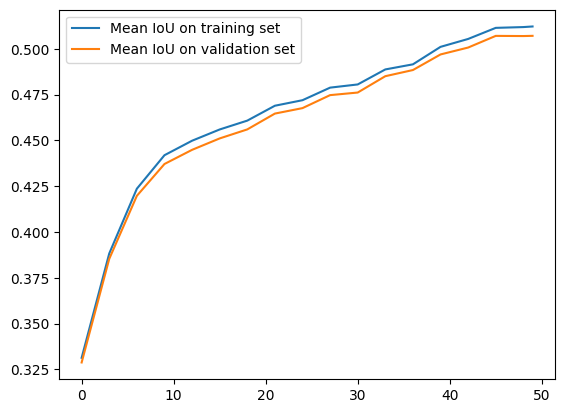
plt.plot(epochs, eval_metrics_history["train_mean_IoU"], label="Mean IoU on training set")
plt.plot(epochs, eval_metrics_history["val_mean_IoU"], label="Mean IoU on validation set")
plt.legend()
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7fb3eeed0490>
Next, we will visualize model predictions on validation data:
model.eval()
val_batch = next(iter(val_loader))
images, masks = val_batch["image"], val_batch["mask"]
preds = model(images)
preds = jnp.argmax(preds, axis=-1)
def display_image_mask_pred(img, mask, pred, label=""):
if img.dtype in (np.float32, ):
img = ((img - img.min()) / (img.max() - img.min()) * 255.0).astype(np.uint8)
fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 5, figsize=(15, 10))
axs[0].set_title(f"Image{label}")
axs[0].imshow(img)
axs[1].set_title(f"Mask{label}")
axs[1].imshow(mask)
axs[2].set_title("Image + Mask")
axs[2].imshow(img)
axs[2].imshow(mask, alpha=0.5)
axs[3].set_title(f"Pred{label}")
axs[3].imshow(pred)
axs[4].set_title("Image + Pred")
axs[4].imshow(img)
axs[4].imshow(pred, alpha=0.5)
for img, mask, pred in zip(images[:4], masks[:4], preds[:4]):
display_image_mask_pred(img, mask, pred, label=" (validation set)")
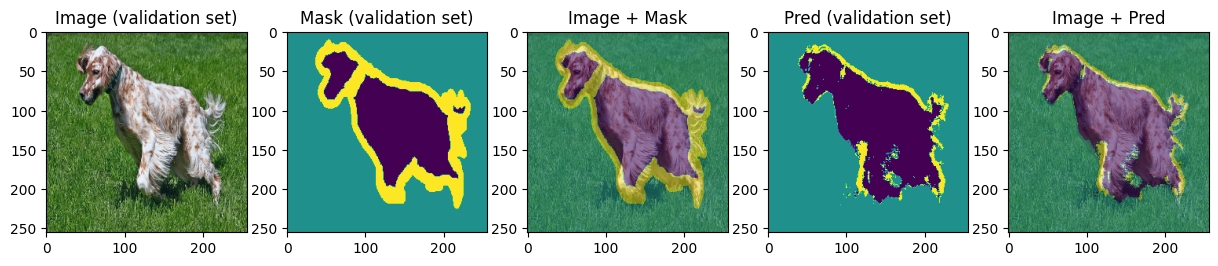

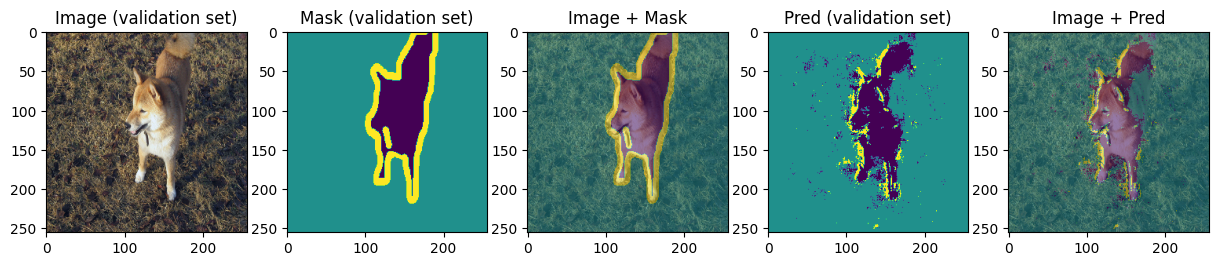
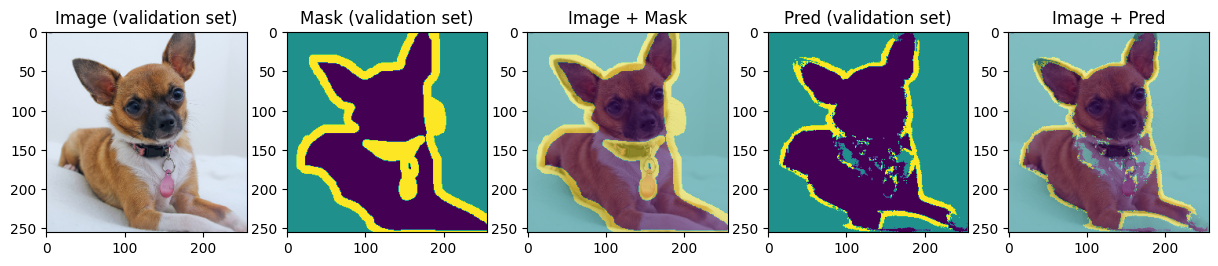
We can see that model can roughly predict the shape of the animal and the background and struggles with predicting the boundary. Carefully choosing hyperparameters we may achieve better results.